Describe a Simple Atwoods Machine Using the Diagrahm
Two in fact one for each mass. Masses m1and m2are connected by a string which runs over a pulley and mass m2sits on a smooth inclined plane.
Begin with the two masses m 1 and m 2 each equal to 50 grams this may be the mass of the hangers alone.

. Also known as two masses on a pulley. The environment allows a user to change the amount of mass. What is the acceleration of the two masses.
Keys to solving Atwood Machine problems are recognizing that the force transmitted by a string or rope known as tension is constant throughout the string and. Gy 32 v 1 2. The machine typically involves a pulley a string and a system of masses.
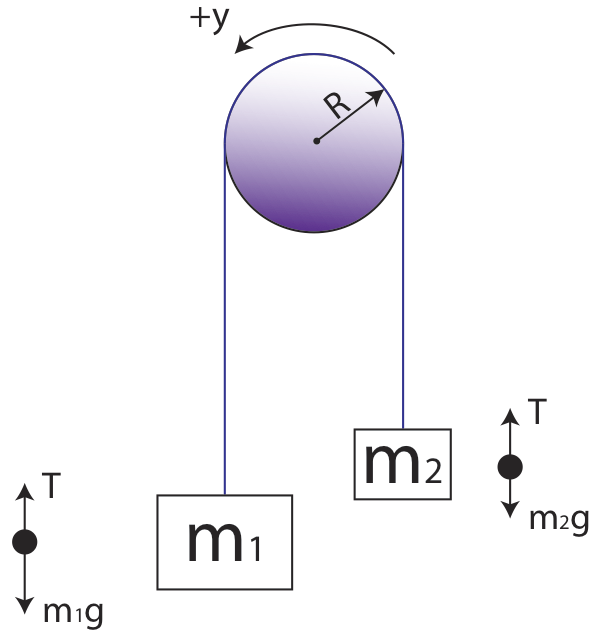
The pulley has no mass and the string has no mass and is inextensible. An Atwoods Machine is a simple device consisting of a pulley with two masses connected by a string that runs over the pulley. 521 Draw separate free-body diagrams for m.
Lab manual Describe a simple Atwoods machine using the diagram. Determine the tension T at rest - In the force vs. The acceleration of the two masses is given by g m m m m a 1 2 1 2.
Surprisingly this simple device comes up. 04d Atwoods MachineRVS-Revised - 2 - Atwoods Machine a technologically useful device for the determination of the acceleration due to gravity. When the two masses are equal the net force is zero.
First of all i have a question regarding a simple Atwoods machine. Atwoods machine is a device where two masses M and m are connected by a string passing over a pulley. An Atwoods machine two masses connected by a string that stretches over a pulley and a modified version of the Atwoods machine one of the masses is on a horizontal surface can be explored.
Atwoods machine is shown schematically in Figure 1. Lab manual Describe a simple Atwoods machine using the diagram. He would be unable to compute the angular momenta of the two masses in respect to O without treating the.
This is how an elevator is constructed. Time diagram highlight the data points measured before release of the cart. If one of the masses is greater than the other eg m1 m2 in figure 1 the system moves as shown.
When the suspended masses are unequal the system will accelerate in the direction of the larger mass. One cannot use separate systems because he would not be able to get the angular momentum with respect to the z axis drawn on the diagram. A m 2 m 1 g m 1 m 2.
Hangers the masses you will use the pulley and the string. 521 Draw separate free-body diagrams for m and m2. Where we take m2 as the larger mass and m1 as the smaller it doesnt really matter as long as we know that positive acceleration is in the direction of the larger mass.
A 4 2 K g 98 m s 2 2 4 K g. Assuming that the pulley has no mass the string has no mass and doesnt stretch and that there is no friction the net force on M1 is the difference between the tension and M1 g TM1 g. The Atwoods Machine 1.
521 Consider the net forces including the tension on each object and combine the. A system of objects consists of all objects within a closed. This device consists of two blocks connected by a light string running over a massless pulley suspended some distance above a floor or table.
One at either end of the string. The heavier weight has mass M15 kg and the lighter weight has mass M2 2 kg. The total kinetic energy of both together is 13 83mgy 93mgy 3mgy which equals the total change in.
Shows how to calculate the acceleration of an Atwood Machine using Newtons second law of motion. The use of Atwoods machine in illustrating the principles of the application of Newtons second law to a simple physical system whose connected parts have both rotational and translational motion is shown. 521 Consider the net forces including the tension on each object and combine the.
V 1 23gy v 2 2 23gy The kinetic energy of m is 12m 23gy 13mgy. Also record the given 500g total mass of the cart and sensors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website http.
Plugging in our masses and g 98 ms 2 gives. A m2- m1 g m1 m2 ExampleNow lets consider an inclined Atwoods machine. Instead it is a disk of radius 01 m and mass M3 kg.
Use pad to protect the floor from impacts. Atwoods Machine Revisited Consider a realistic Atwoods machine where the pulley is not massless. If the masses are not equal then the system of masses will accelerates.
Use a piece of string long enough that you can observe the mass falling at least 1 meter. Identify the action-reaction pair on the diagrams using Newtons Third Law. Atwoods machine is the name of a device that looks like this.
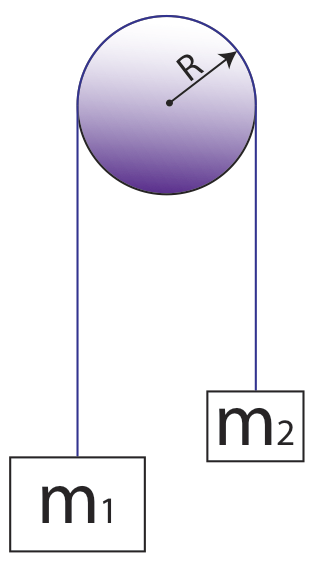
1 Simple Atwoods machine. Using a triple beam balance verify the value of the hanging mass m and record the value in the Data Table below. An Atwoods machine is simply two masses hanging over a pulley.
The kinetic energy of 2m is 122m4 23gy 83mgy. 1 Simple Atwoods machine. The Atwoods Machine Interactive provides an environment that allows the learner to explore two-mass systems.
If one pulley is suspended from a fixed support and it has 2 masses. Atwoods machine in free fall. The system is released from rest when the lighter mass is on the floor and the.
In this experiment you will measure the acceleration and compare to. If i construct a free-body diagram of the pulley it has 2 forces. Start with a good free-body diagram.
Assume that M m. In the free body diagram of the Atwoods machine T is the tension in the string M1 is the lighter mass M2 is the heavier mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity. Remember smooth is just a code word for frictionless.
The Atwoods Machine is a simple machine that consists of a pulley of negligible mass and friction over which two masses are suspended. An Atwood Machine is a basic physics laboratory device often used to demonstrate basic principles of dynamics and acceleration. For an ideal Atwoods Machine we assume the pulley is massless and frictionless that the string is unstretchable therefore a constant length and.
The pulley is considered to be frictionless. Equation 1 You will derive this formula from the application of Newtons 2 nd Law to the Atwood Machine. Identify the action-reaction pair on the diagrams using Newtons Third Law.

Solved 1 Simple Atwood S Machine A Lab Manual Describe Chegg Com

Solved 1 Simple Atwood S Machine A Lab Manual Describe Chegg Com
0 Response to "Describe a Simple Atwoods Machine Using the Diagrahm"
Post a Comment